
Mastering Cybersecurity: AdvancedTechCo Unveils Strategies to Tackle Zero-Day Vulnerabilities
In the rapidly evolving landscape of cybersecurity, zero-day vulnerabilities stand out as enigmatic threats that keep security experts on their toes. These vulnerabilities are shrouded in mystery, often exploited by malicious actors before developers can even detect and patch them. In this blog, we’ll delve into the world of zero-day vulnerabilities, exploring what they are, why they are a significant concern, and how the cybersecurity community, including companies like AdvancedTechCo, works to address this ever-present challenge.
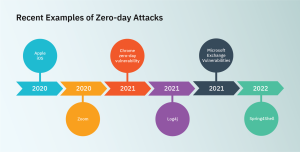
Understanding Zero-Day Vulnerabilities:
A zero-day vulnerability refers to a security flaw in software, hardware, or firmware that is unknown to the vendor or the public. The term “zero-day” signifies that developers have had zero days to fix the issue, leaving users exposed to potential exploitation. These vulnerabilities can exist in operating systems, applications, browsers, or even embedded systems.
The Life Cycle of a Zero-Day Vulnerability:
1. Discovery: Zero-day vulnerabilities are typically discovered by security researchers, ethical hackers, or malicious actors. The initial discovery is often kept confidential to prevent widespread exploitation.
2. Exploitation: Malicious actors exploit zero-day vulnerabilities to compromise systems, steal data, or carry out cyberattacks. The targeted nature of these attacks makes them particularly dangerous.
3. Disclosure: Once a zero-day vulnerability is discovered, ethical hackers may choose to disclose it responsibly to the vendor. This initiates the process of developing and releasing a patch to fix the vulnerability.
4. Patch Development and Release: Developers, including companies like AdvancedTechCo, work to create a patch that addresses the vulnerability. The patch is then released to the public through software updates or security advisories.
5. User Adoption of Patch: The effectiveness of patching relies on users promptly applying updates. Unfortunately, not all users are diligent in keeping their software up to date, leaving systems vulnerable even after a patch is available.
Challenges Associated with Zero-Day Vulnerabilities:
1. Limited Detection: Zero-day vulnerabilities often go undetected for extended periods because they are unknown to security vendors and software developers.
2. Targeted Attacks: Malicious actors exploit zero-day vulnerabilities in targeted attacks, making it challenging for traditional security measures to detect and prevent these attacks.
3. Economic and Strategic Value: Zero-day vulnerabilities are highly valuable in the cyber underground. They can be sold on the dark web or used by state-sponsored actors for espionage or sabotage.
Addressing the Zero-Day Challenge:
1. Vulnerability Disclosure Programs: Responsible disclosure is crucial in addressing zero-day vulnerabilities. Many organizations, including AdvancedTechCo, and security researchers participate in coordinated disclosure programs to alert vendors without putting users at risk.
2. Security Best Practices: Users and organizations can mitigate the risk of zero-day exploits by adopting security best practices, such as regular software updates, network segmentation, and employee training.
3. Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS): Deploying advanced intrusion detection systems helps identify anomalous behavior that may indicate a zero-day attack.
Conclusion:
Zero-day vulnerabilities remain a formidable challenge in the cybersecurity landscape. As technology advances, the need for proactive security measures, responsible disclosure, and user awareness becomes more critical than ever. Companies like AdvancedTechCo play a pivotal role in unraveling the mystery surrounding zero-day vulnerabilities, contributing to a more secure digital environment.

 Phone:
Phone:
0 comment